| Nickel-iron-chromium alloys that have the same basic composition as INCOLOY alloy 800 but with significantly higher creep-rupture strength. The higher strength results from close control of the carbon, aluminum and titanium contents in conjunction with a hightemperature anneal. Used in chemical and petrochemical processing, power plants for super-heater and reheater tubing, industrial furnaces and heat-treating equipment. |
| Standard Product Forms |
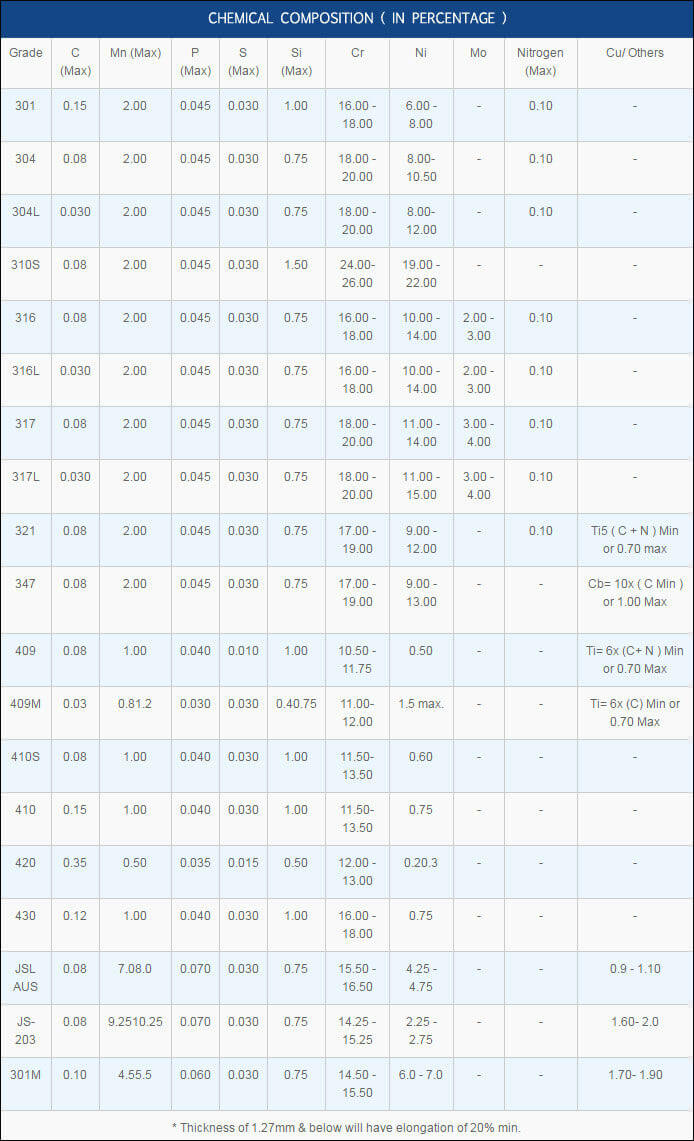
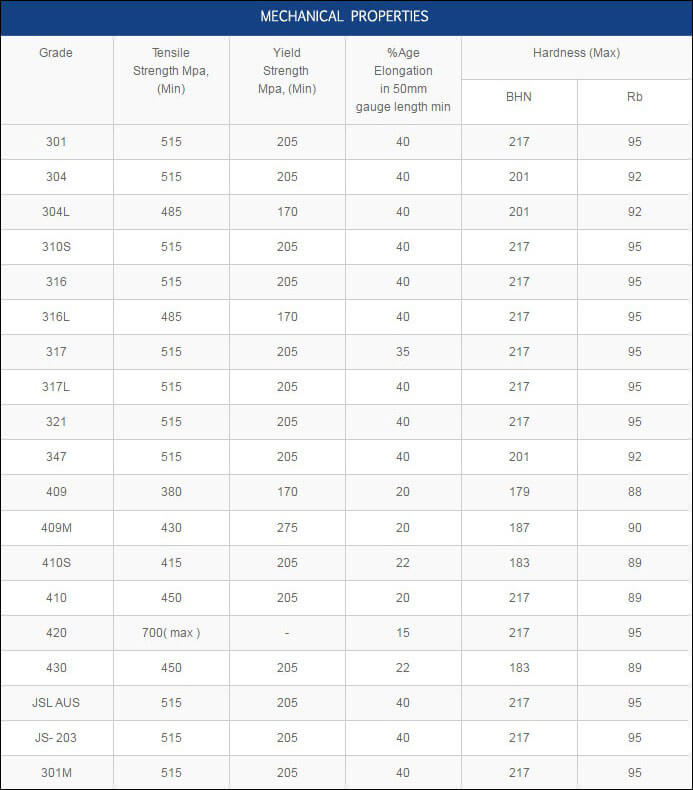
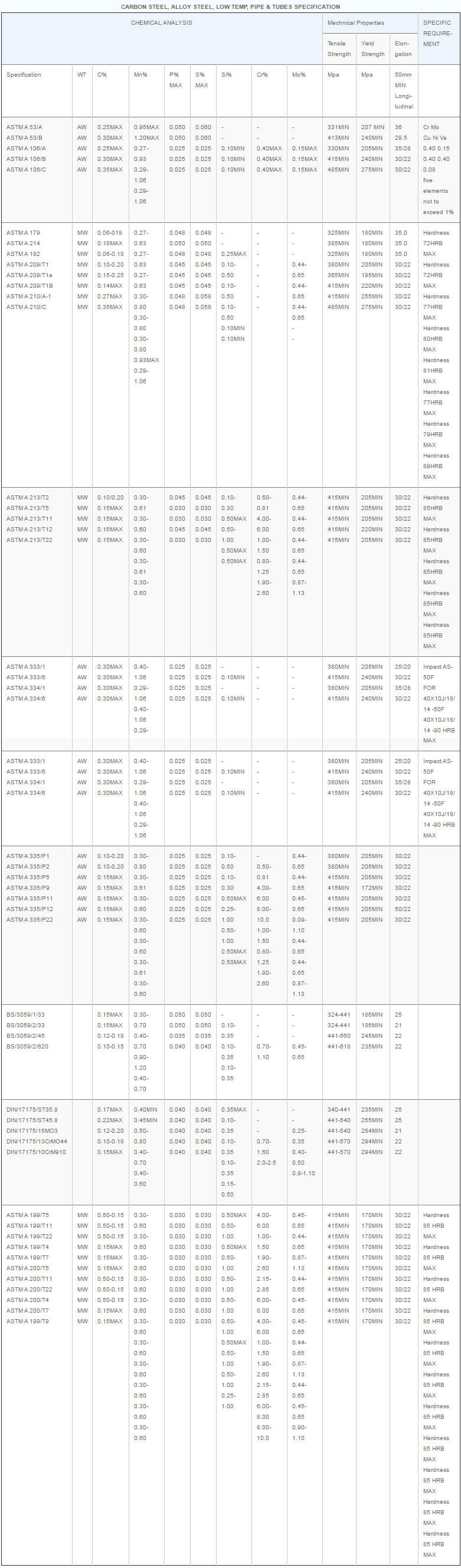
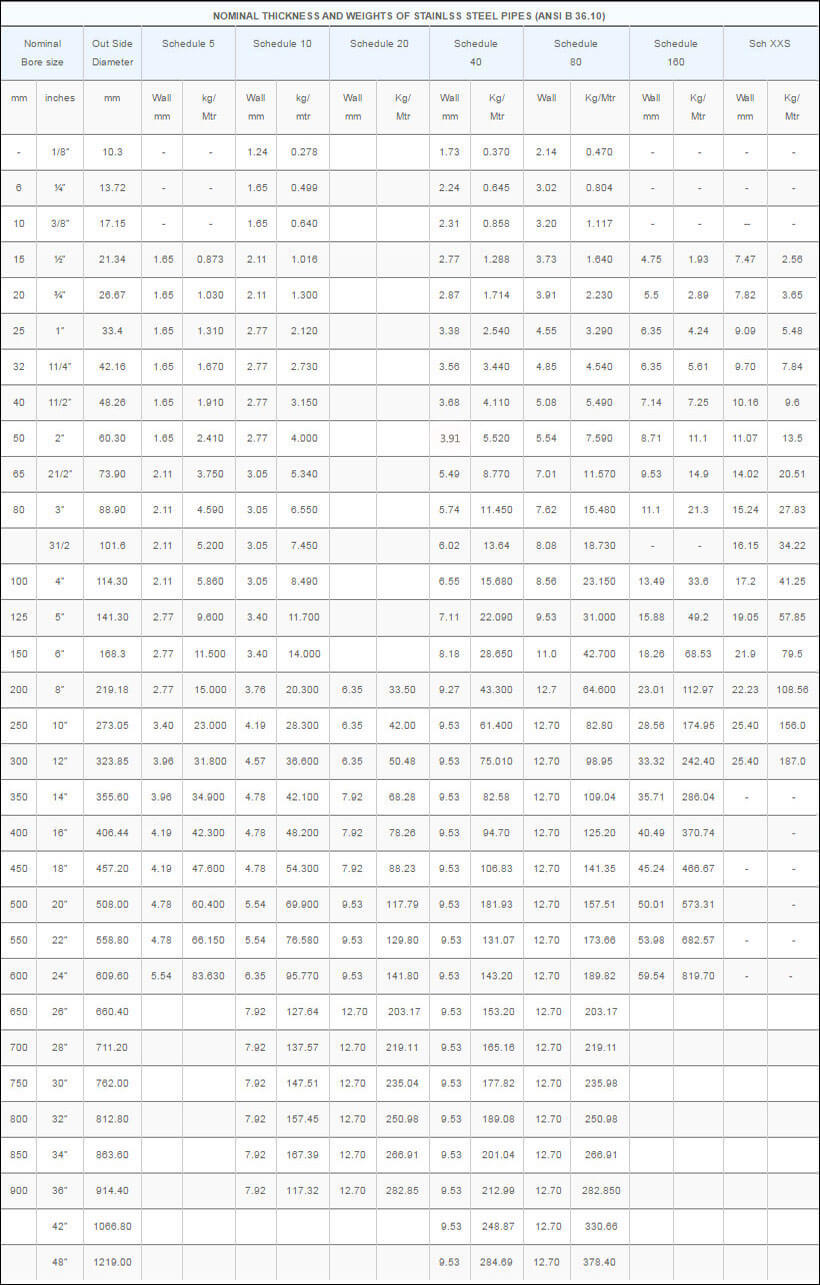
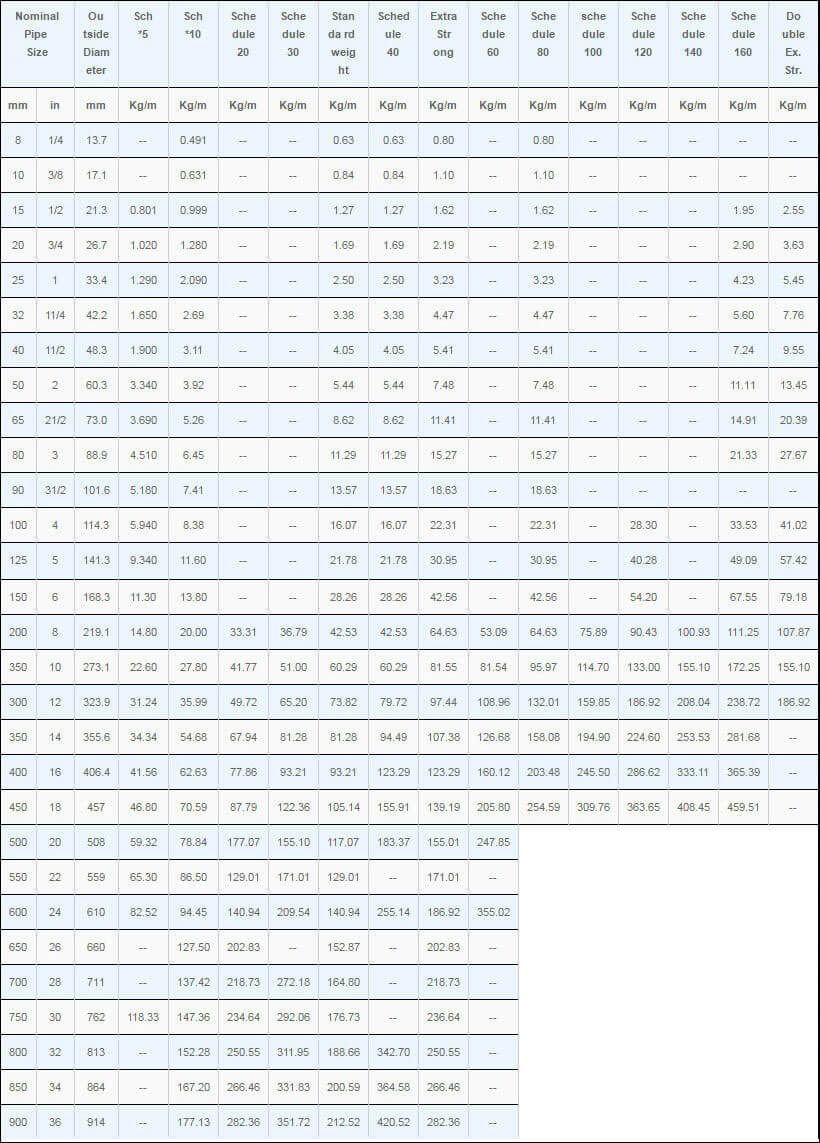
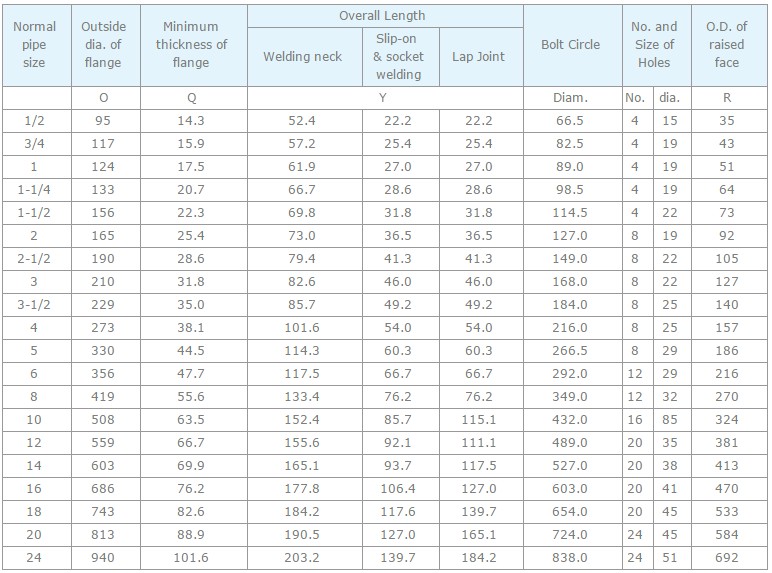
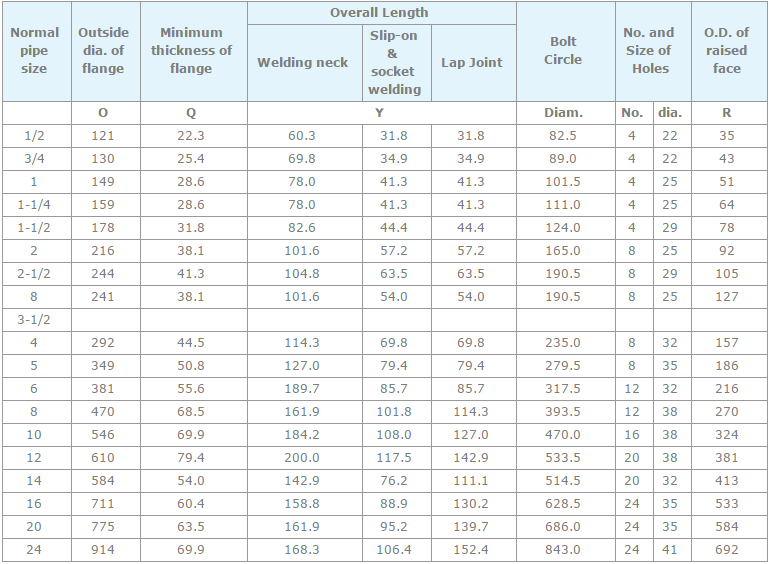
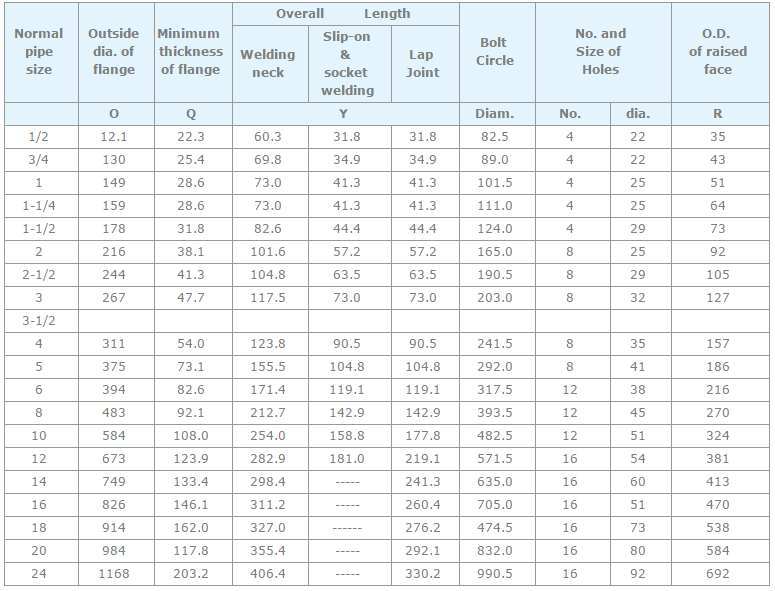
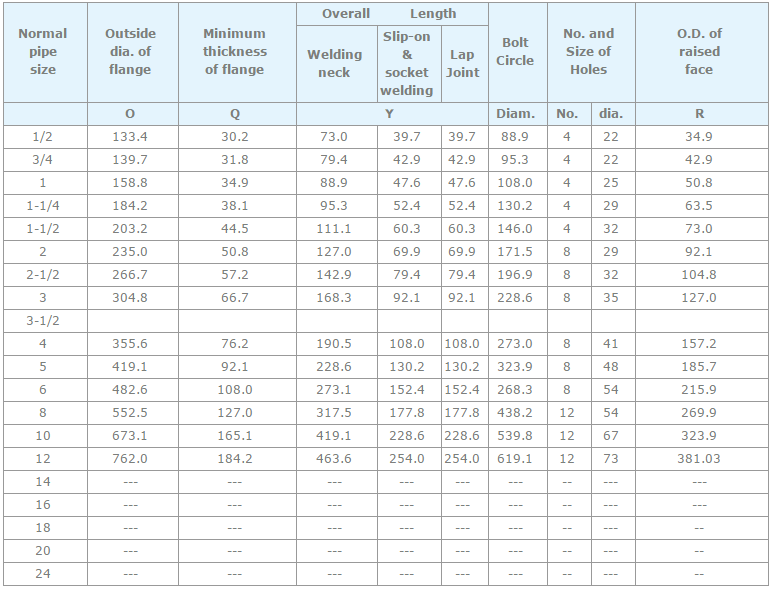
Pipe, tube, sheet, strip, plate, round bar, flat bar, forging stock, hexagon and wire. |
| Major Specifications: |
| UNS |
N08810, N08811 |
| BS |
3072, 3073, 3074, 3075, 3076 (NA15) |
| ASTM |
A240, A480, B163, B366, B407–409, B514, B515, B564, B751, B775, B829 |
| ASME |
SA-240, SA-480, SB-163, SB-366, SB-407–409, SB-514, SB-515, SB-564, SB-751, SB-775, SB-829 |
| ASME Code Cases |
1325, 1949, 1983, 2339, N-201, N-254 |
| DIN |
17459, 17460 |
| Werkstoff Nr. |
1.4876, 1.4958, 1.4959 |
| VdTÜV |
412, 434 |
| EN |
10028-7, 10095 |
| ISO |
4955A, 6207, 6208 |